Find out how you can digitalize your production
with solutions from MPDV!
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition / SCADA – Smart Factory Glossar
The abbreviation SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. It describes (local) computer systems monitoring and controlling technical processes and visualizing workflows. SCADA systems can be used for multi-site operation. By collecting data across the entire process chain, companies are empowered to take decisions based on recorded data. SCADA therefore is a control system featuring supervision, control, and data collection.
SCADA systems combine hardware and software: programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and remote-control terminals handle most of the control tasks. All status information such as switch positions or sensor values of valves, pumps, or engines are recorded by the software of the SCADA system.
The data is forwarded to the control center where operators monitor the activities of controllers and terminals with the help of human machine interfaces (HMI). These HMIs allow the machine operators to interact with the PLC. For this reason, user interfaces are very important in SCADA systems.
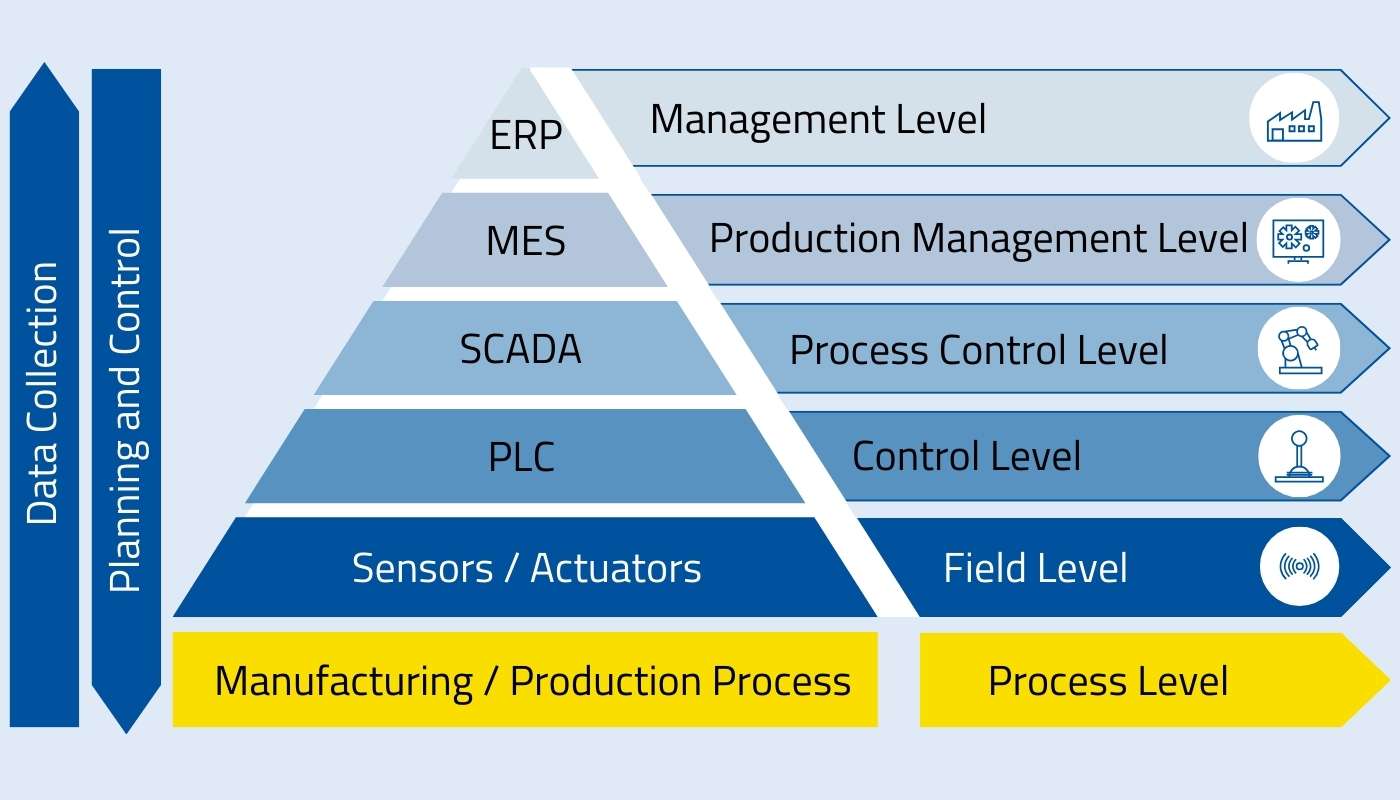
SCADA in the automation pyramid
In a classic automation pyramid, SCADA is assigned to the supervisory level together with Distributed Control Systems (DCS). Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) like MES HYDRA X are part of the higher-level planning level. Compared to SCADA systems that collect, monitor, and control machine data, the MES combines and correlates the data to provide the basis for the management to make well-founded decisions.
Modern manufacturing software goes even further by networking machines, production units, and their controls with an integration platform such as MPDV's Manufacturing Integration Platform (MIP). The integration platform records all data from production and provides it to the MES where the data is processed and analyzed.
SCADA is used for the following purposes:
- Infrastructure processes: Monitoring and controlling processes in the energy and transportation sectors, water supply, electricity, and wind farms.
- Facility processes: Monitoring and controlling of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
- Industrial processes: Monitoring of production, process control, power generation.
Sources
- SCADA: Wikipedia, 06.01.2024 [online] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SCADA (requested on 26.02.2024)
User interface: Wikipedia, 12.02.2024 [online] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User_interface (requested on 26.02.2024)
Would you like more information? We are happy to help.
Just fill in the form below. We will take care of your inquiry promptly.